PhaseZero Interview Experience
Sharing a few PhaseZero interview questions for the Java Developer role. The questions were very basic.
Implementation of Singleton Pattern -
class SingletonImpl{
...
private static singletonInstance = null;
...
private SingletonImpl(){
...
}
public synchronized static getSingleton(){
if(singletonInstance == null) singletonInstance = new SingletonImpl();
return singletonInstance;}
...
}
Note that the Constructor is declared private.
PhaseZero Interview Experience questions -
- What is the difference between Extend and Implement? -
- Extends is used when we are extending the base class. Implements is used when we are implementing an interface.
- A class can extend only one class but can implement any number of interfaces. For example, ArrayList implements 4 interfaces, i.e. List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, and Serializable.
- A class must implement all the methods from an interface.
- What is the difference between Hashmap and Hashtable?
- Hashmap is non-synchronized. It cannot be shared between many threads without proper synchronization code, whereas Hashtable is synchronized. However, Hashmap can be made synchronized by inserting a code.
- Hashmap allows one null key and multiple null values, whereas Hashtable doesn't allow any null key or value.
- Hashmap is comparatively faster than Hashtable.
- Hashmap is traversed by Iterator and Hashtable can be traversed by the Iterator as well as Enumerator.
- Hashmap inherits AbstractMap class whereas Hashtable inherits Dictionary class.
- Difference between ClassNotFoundException vs ClassDefNotFoundException?
When a classpath is not defined with the updated JARS, a runtime exception is thrown which is known as ClassNotFoundException Whereas, like the name says ClassDefNotFoundException, during run time when a class is not declared, an error is thrown saying that ClassDefNotFound, it can be a case, that the class was present at compile time but couldn't be found during runtime.
- How to create customException in Java?
User-defined exceptions can be created in java using the throw keyword.
- What is the root class of Exception?
The answer is Throwable. Please find below block diagram.
- Difference between Interface and Abstract class?
We have already covered this topic in another post.
- Given a table with dept_id and dept_name columns and Student table with name, dept_id and marks, write query to
select students with marks greater than 75 of given dept name.
Select b.marks
from students b
INNER JOIN Department b
ON a.dept_id = b.dept_id Where marks > 75;
- Final methods and variables in Java?
Final is a keyword that can be applied to variables, methods, classes and local variables in java the value assigned cannot re-initialized. A method or class used with the Final keyword cannot be over-ridden.
- Difference between the Singleton and Factory design patterns?
Singleton design pattern is a pattern in java where a single instance of a class is created and a single object is used by all other classes. For instance, a single DB connection shared by all other classes.
Implementation of Singleton Pattern -
class SingletonImpl{
...
private static singletonInstance = null;
...
private SingletonImpl(){
...
}
public synchronized static getSingleton(){
if(singletonInstance == null) singletonInstance = new SingletonImpl();
return singletonInstance;}
...
}
Note that the Constructor is declared private.
Factory Design Pattern- Factory design patterns creates a new instance of the object whenever the factory method is being called.
- What are the different ways of creating objects?
There are basically 4 different ways using which we can create an object in Java -
- By using the new keyword
- using Class.forName() keyword
- using Clone()
- using object deserialization
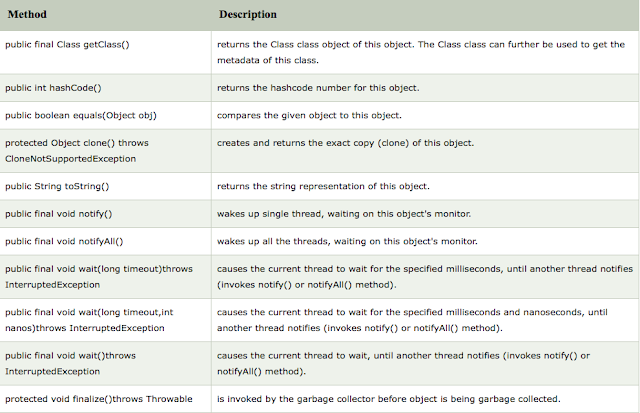
- What are the different methods in Object Class?
There are lots of methods used in Object class, some of them are listed below -
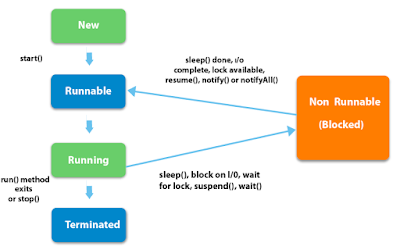
- Explain the life cycle of thread?
There are 5 states of Thread life-cycle -
- Difference between Start() and Run() method?
When program calls start() method, a new thread is created and code inside Run() method is executed in a new thread, while run() method will create no new thread and code inside Run() will execute in the current method.

Comments
Post a Comment